What is Genomics ?
The study of an organism’s entire genome is known as genomics, and it incorporates concepts from genetics. Recombinant DNA, DNA sequencing techniques, and bioinformatics are all combined in genomics to sequence, assemble, and analyse the structure and function of genomes. In contrast to “classical genetics,” it takes into account all of an organism’s genetic makeup rather than just one gene or one gene product at a time. Additionally, bumi genomics is concerned with interactions across loci and alleles in the genome as well as additional interactions like epistasis, pleiotropy, and heterosis. Since Fred Sanger’s groundbreaking work and more current next-generation sequencing technology have made it possible, BGI Malaysia has taken advantage of the availability of whole DNA sequences for entire organisms.

In the 1970s and 1980s, Fred Sanger’s team developed tools for genome mapping, sequencing, data storage, and bioinformatic studies. The human genome project, a tremendous accomplishment of international cooperation that culminated in the publishing of the full human genome sequence in 2003, was made possible thanks to the work done in the 1980s. The speed, volume, and price of genome sequencing have all dramatically increased thanks to the development of next-generation sequence technologies. Additionally, hundreds of life-science databases and programs that promote scientific study have been made possible because to advancements in bioinformatics. These databases make it simple to search, contrast, and evaluate the information that is saved and structured there. In the sections that follow in this course, Bumi Genomics Innovation Sdn Bhd will look at some important genomics resources.
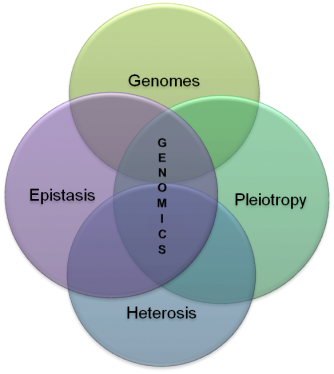
and other intragenomic interactions.
Common study types in functional Genomics.
- Transcription profiling
- Genotyping
- Epigenetic profiling
- DNA/RNA-protein interaction
- Meta-analysis





